Late Paleozoic in situ microorganisms in chert deposits
Section Palaeobotany
Microorganisms are critical in the bio- and geosphere today, and are responsible for the sustainability of ecosystem functions ranging from decomposition and bioerosion, to the catalyzation of nutrient cycles. With this recognition of the significance of microorganisms today, detailed knowledge about the evolutionary history of these organisms and their roles in biological and ecological processes in the past is pivotal to understanding the sustainability and evolution of ancient ecosystems.
Chert deposits are among the most important sources of information about fossil microorganisms, and about microbial associations and interactions with other organisms in ancient ecosystems. This is due primarily to the fact that cherts represent a mode of preservation in which the morphology, anatomy, and diversity levels of not only the microorganisms, but also their host organisms can be directly examined. Moreover, aspects of microbial biology and ecology (e.g., life history features, habitat preferences), as well as specific details of microbial associations and interactions (e.g., infection pathways, spatial distribution of the microbes on/within the host, host responses), can often be demonstrated on a consistent basis from multiple examples.
Our research currently centers around three chert deposits containing exquisitely preserved terrestrial plants and microorganisms.
• The Early Devonian Rhynie chert (Aberdeenshire, Scotland)
• The Visean (Late Mississippian) cherts of Esnost and Lay/Roanne (France)
• The Late Pennsylvanian Grand’Croix cherts (central France)
The fossil communities preserved in these cherts are used to document the morphology, biology, and biodiversity of the microorganisms, and also to detail the biological interactions between different types of microorganisms and between microorganisms and terrestrial plants. It is interesting to note that, although none of the plant partners exist today, many of the microorganisms involved appear morphologically little changed. Moreover, some interactions suggest that the genetic code and biochemical pathways necessary for the interactions to be successful evolved early in the lineages of microorganisms involved, and have seemingly remained unchanged to the present. The examination of inter-microbial and microorganism-land plant associations and interactions provides another level of biological resolution that helps in formulating hypotheses designed to more fully understand the functioning and evolution of ecosystems.
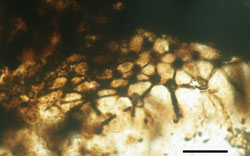
Abb. A: Ausschnitt aus einer L. macrosporae Kolonie (rechts); Maßstab 40 μm [aus: KRINGS et al. (2005), Geobios 38: 451–465] 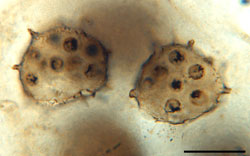
Abb. C: Reproduktionsstrukturen eines bislang unbeschriebenen, pilzähnlichen Mikroorganismus aus dem Rhynie Chert (Unterdevon, Schottland); Maßstab = 25 μm. [aus: KRINGS et al. (2007), New Phytol. 174: 648–657] 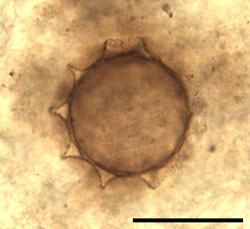
Abb. E: Phycoma einer Prasinophycee aus dem Rhynie Chert; Maßstab = 40 μm 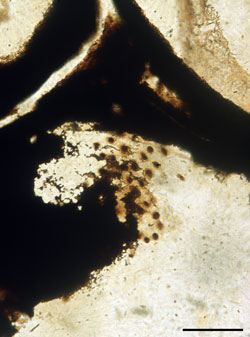
Abb. A: Ausschnitt aus einer Sublagenicula nuda Megaspore aus dem Visé (oberes Unterkarbon) von Frankreich mit einer Kolonie der endophytischen Alge Lageniastrum macrosporae Maßstab = 100 μm. [aus: KRINGS et al. (2005), Geobios 38: 451–465] 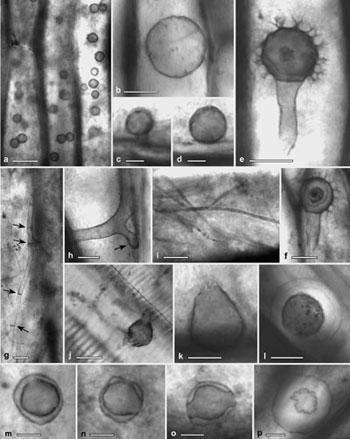
Abb. B: Hyphen (g–i), Sporen (a,b,m–p) und Fruktifikationen (c–f,j–l) verschiedener Mikropilze und pilzähnlicher Mikroorganismen aus dem Holz und Periderm einer Lycophyte (Lepidodendron rhodumnense) aus dem Visé (oberes Unterkarbon) von Frankreich; Maßstäbe = 5 μm (c,d,m–o), 10 μm (g–i,k,p), 20 μm (a,b,e,f,l) und 40 μm (j). 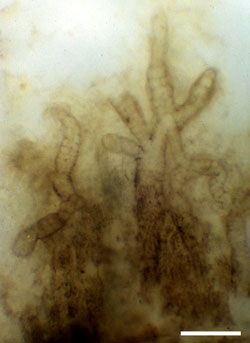
Abb. D: Filamente einer bislang unbeschriebenen Cyanobakterie aus dem Rhynie Chert; Maßstab = 20 μm.
Scientific cooperation
- Hans Kerp & Hagen Hass, Forschungsstelle für Paläobotanik am Geologisch-Paläontologischen Institut, Westfälische Wilhelms-Universität Münster, Hindenburgplatz 57, 48143 Münster, Germany.
- Thomas N. Taylor, Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology, and Natural History Museum and Biodiversity Research Center, The University of Kansas, Lawrence, KS 66045-7534, U.S.A.
- Jean Galtier, AMAP, UMR 5120 CNRS, CIRAD TA A-51/ PS2, Boulevard de la Lironde, 34398 Montpellier, France.
- Reinhard Agerer, Department Biologie I und GeoBio-CenterLMU, Organismische Biologie: Mykologie, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, Menzinger Straße 67, 80638 Munich, Germany.
- Several other colleagues in individual projects. University of Kansas at Lawrence, USA.
Funding
- Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG)
- National Science Foundation (NSF)
- Alexander von Humboldt-Foundation
- Freunde der Bayerischen Staatssammlung für Paläontologie und Historische Geologie, München e.V.
Publications
Dotzler N, Krings M, Agerer R, Galtier J, Taylor TN (2008) Combresomyces cornifer gen. sp. nov., an endophytic peronosporomycete in Lepidodendron from the Carboniferous of central France. Mycological Research 112, 1107–1114.
Dotzler N, Walker C, Krings M, Hass H, Kerp H, Taylor TN, Agerer R (2009) Acaulosporoid glomeromycotan spores with a germination shield from the 400-million-year-old Rhynie chert, Mycological Progress 8, 9–18.
Krings M, Dotzler N, Galtier J, Taylor TN (2009) Microfungi from the upper Visean (Mississippian) of central France: Chytridiomycota and chytrid-like remains of uncertain affinity. Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology 156, 319–328.
Krings M, Dotzler N, Taylor TN (2009) Globicultrix nugax nov. gen. et nov. spec. (Chytridiomycota), an intrusive microfungus in fungal spores from the Rhynie chert. Zitteliana A 48/49, 165–170.
Krings M, Dotzler N, Taylor TN, Galtier J (2007) A microfungal assemblage in Lepidodendron from the Upper Visean (Carboniferous) of central France. Comptes Rendus Palevol 6, 431–436.
Krings M, Dotzler N, Taylor TN, Galtier J (2009) A Late Pennsylvanian fungal leaf endophyte from Grand-Croix, France, Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology 156, 449–453.
Krings M, Galtier J, Taylor TN, Dotzler N (2009) Chytrid-like microfungi in Biscalitheca cf. musata (Zygopteridales) from the Upper Pennsylvanian Grand-Croix cherts (Saint-Etienne Basin, France). Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology 157, 309–316.
Krings M, Hass H, Kerp H, Taylor TN, Agerer R, Dotzler N (2009) Endophytic cyanobacteria in a 400-million-yr-old land plant: A scenario for the origin of a symbiosis? Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology 153, 62–69.
Krings M, Kerp H, Hass H, Taylor TN, Dotzler N (2007) A filamentous cyanobacterium showing structured colonial growth from the Early Devonian Rhynie chert. Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology 146, 265–276.
Krings M, Taylor TN, Dotzler N, Decombeix AL (2010) Galtierella biscalithecae nov. gen. et sp., a Late Pennsylvanian endophytic water mold (Peronosporomycetes) from France. Comptes Rendus Palevol 9, 5–11.
Krings M, Taylor TN, Hass H, Kerp H, Dotzler N, Hermsen EJ (2007) An alternative mode of early land plant colonization by putative endomycorrhizal fungi. Plant Signaling & Behavior 2, 125–126.
Krings M, Taylor TN, Hass H, Kerp H, Dotzler N, Hermsen EJ (2007). Fungal endophytes in a 400-million-yr-old land plant: infection pathways, spatial distribution, and host responses. New Phytologist 174, 648–657.
Taylor TN, Krings M (2005) Fossil microorganisms and land plants: associations and interactions. Symbiosis 40, 119–135.
Taylor TN, Krings M (2010) Paleomycology: the rediscovery of the obvious. Palaios 25, 283–286.