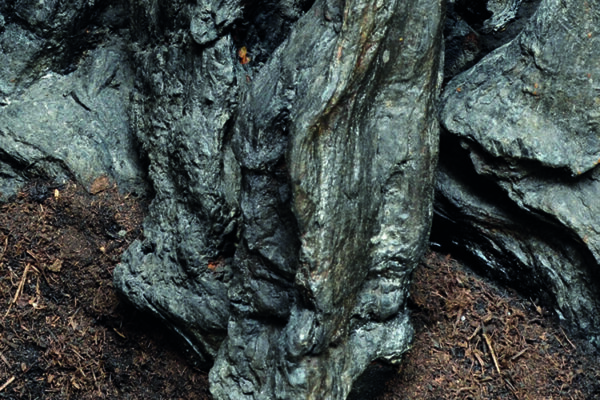
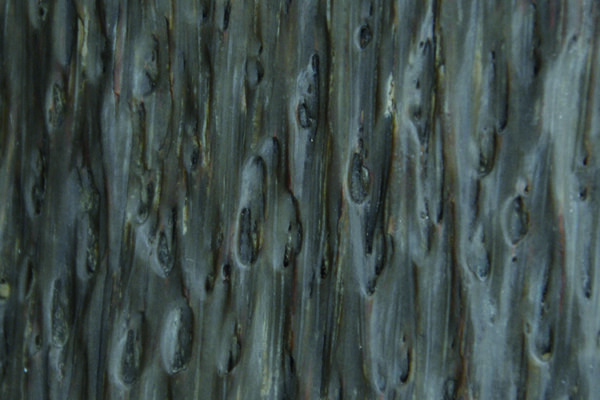
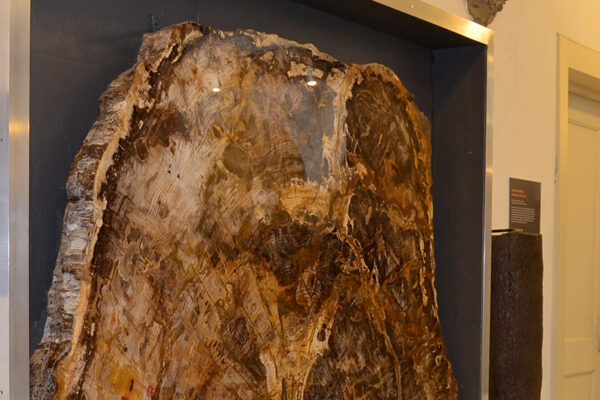
Palm Trunk
Palmoxylon aschersonii

Neogene: Miocene, approx. 20 Mio. years old
Area of Abu Roash near Cairo, Egypt
Silicified remains of palms occur in Cretaceous and Cenozoic sediments worldwide. Palm trunks differ from the trunks of conifers and deciduous trees in that they do not have a coherent woody body, but consist entirely of individual conducting bundles surrounded by strengthening tissue, held together by a matrix of thin-walled cells, which are easily recognizable in the fossil as thin tubes.
SNSB-BSPG 1981 I 100
Original